Second Law of Motion
Second Law of Motion: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Momentum, Unit of Force, SI Unit of Momentum, Second Law of Motion, Change in Momentum, Mathematical Formulation of Second Law of Motion, Mass of a Body and, One Unit of Force
Important Questions on Second Law of Motion
Write down the formula of momentum.
In how much time an object having mass of will speed up from if force will be applied to it
In CGS system is equal to _____.
When we apply a force of , we can hold a body whose mass is approximately equal to
The momentum of a body of mass is . Its kinetic energy is
The change in momentum of a body in is . The force acting on it is
If an object of mass experience a force of , the acceleration produced by it is.
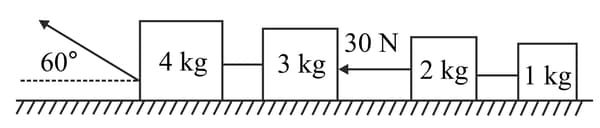
Figure shows four blocks that are pulled along a smooth horizontal surface. The masses of the blocks and tension in one cord are given. The pulling force is
How many dynes are there in ?
Assertion: We should always wear a seat belt while travelling in a car.
Reason: Seat belt prevents us from falling forward due to inertia when sudden brakes are applied.
A loaded lorry of mass moves with a velocity of . Its velocity becomes after . What is the rate of change of momentum?
A loaded lorry of mass moves with a velocity of . Its velocity becomes after . Calculate the change in momentum.
A loaded lorry of mass moves with a velocity of . Its velocity becomes after . The final momentum will be:
A loaded lorry of mass moves with a velocity of . Its velocity becomes after . The initial momentum will be:
A car rolls down a hill with an acceleration of . If the mass of the car is , calculate the unbalanced force that acts on the car.
The momentum is the product of mass and _____.
When a body travels at uniform velocity, its momentum changes by _____ .
In the equation , will become one for one unit of force. One unit of force is also equal to one _____.
Consider the equation . The unit of force is so chosen that the value of the constant, becomes _____.
